Data Perimeter: Insights from AWS Summit Paris 2024

I was thrilled to participate to the AWS Summit Paris this year, and to be able to connect with skilled individuals and attend interesting sessions treating diverse subjects.
If you attended the Summit this year, you likely noticed that it was primarily centered around data and AI.
Among the various sessions I attended, my attention was particularly drawn to those addressing data protection, which will be the topic I’ll delve into in this blog article.
One standout session explored the implementation of a data perimeter on AWS, showcasing Societe Generale’s approach to deploying perimeter controls using services and features such as IAM, SCP, and VPC endpoints policies.
The speakers, Claude Ampigny and Achraf Moussadek Kabdani from AWS, along with Al’hossein Laaguel from Société Générale, shared valuable insights on this topic.
No doubt that robust data security measures have become crucial in order to mitigate risks such as data disclosure, so let’s explore the key insights shared during this enlightening session.
Before diving into the implementation, it is important to note that the data perimeter does not replace the standard security measures that must be implemented, rather, it serves as an additional layer.
So, what exactly is a data perimeter on AWS?
A data perimeter consists of preventive guardrails that ensure only trusted identities access trusted resources from expected networks. It involves implementing controls on identities, resources, and networks to uphold these security conditions.
Essentially, these controls define the boundaries within which data can flow, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorised access or breaches.
Setting up a perimeter involves several steps:
- outlining security objectives,
- defining trusted identities, resources, and expected networks,
- conceiving data perimeter controls while anticipating potential side effects,
- and finally implementing these controls within your AWS organization, with continuous monitoring for improvement.
Perimeter controls enable the achievement of six specific security objectives through various combinations of IAM policy types and condition keys:
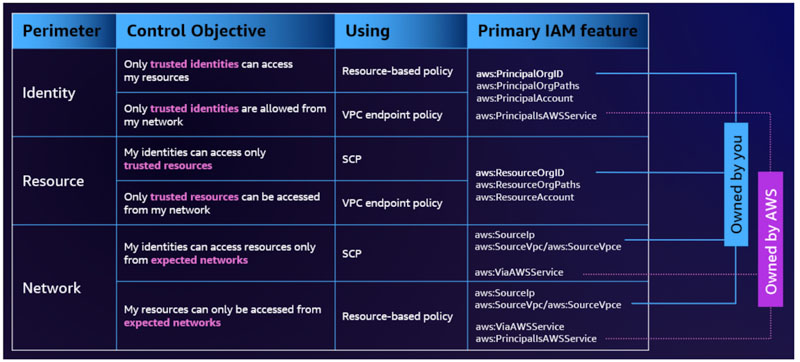
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/fr/identity/data-perimeters-on-aws/
For instance, the identity perimeter effectively mitigates various security risks, such as unintended data disclosure. The IAM condition keys outlined in this table help control access by determining whether the IAM principal belongs to a particular account or an organization.
To help implement the data perimeter controls, AWS provides a Github repository containing a set of policy examples that can help achieve the stated objectives.
Additionally, AWS has developed a tool called Data perimeter helper, which assists in anticipating the potential effects of implementing data perimeter controls by analyzing access activity recorded in CloudTrail logs. Note that data events need to be enabled in CloudTrail for services supporting them if you want to analyze the associated API calls.
Following implementation, a monitoring phase shall begin to assess the potential impact of the measures deployed.
Key takeways on implementation
The key takeaways shared by the Societe Generale representative for organizations seeking to enhance their data perimeter controls are the following:
- Prioritize AWS services with the highest risk and usage rates, such as S3.
- Adapt the data perimeter and its deployment to suit your constraints and budgets
- Accompanying the change; proactively anticipate the impacts of implementing controls, handle exceptions, particularly concerning legitimate third-party access for partners.
- Implement quick wins such as establishing a resource perimeter via SCP
- Thoroughly analyze AWS services and their functionalities to ensure effective control implementation.
- Acknowledge that your security does not solely rely on the data perimeter
In conclusion, establishing a data perimeter on AWS plays a critical role in safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches. However, it’s essential to understand that it does not replace standard security measures; rather, it complements them as an additional layer of protection.
Throughout this journey of implementation, organizations must meticulously outline their security objectives, define trusted identities, resources and expected networks, and define data perimeter controls while anticipating potential side effects. Continuous monitoring and refinement of these controls are imperative to adapt to evolving threats and maintain an effective perimeter over time.







